Now you can 3-D Print
Objects made of Wood Fibers.
Cellulose offers
sustainable Alternative to Metal and Plastic.
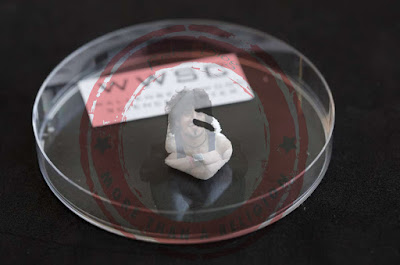 |
A tiny 3D
printed chair made of cellulose.
|
From prosthetic hands to
an entire bridge, you can pretty much 3D print anything you can imagine. But
the materials to make them are diversifying a bit more slowly. Now researchers
from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have found a way to 3D print
objects from cellulose, a naturally occurring string of molecules derived from
wood. The resulting objects are an environmentally friendly and sustainable
alternative to the metals and plastics that currently dominate 3D printing. The
researchers presented their work this week at a conference titled “New
Materials From Trees.”
We’re used to seeing objects
and constructions made of wood, but it hasn’t been easy to put it in a form
that can be 3D printed. Unlike the metal or plastic commonly used in 3D
printing, cellulose doesn’t melt when heated, which means it’s much harder to
mold into different objects. To work around this, the researchers mixed tiny
fibers of cellulose in a liquid gel made of water. The researchers tested their
mixture on a 3D bio-printer, which had been used previously to make scaffolds where cells grew before being implanted in a patient.
Once the object has been
printed from the gel, it has to dry, which is critical for maintaining its
final shape. The researchers figured out a way to freeze the object, then
slowly remove some of the water so that the final product is in the desired
shape.
The researchers were also
able to insert carbon nano-tubes into the dry object so that it could conduct electricity. When they tested one conductive gel with the nano-tubes and one
without, they were able to create a 3D electrical circuit.
Found in the cell walls of
plants and algae or secreted by bacteria, cellulose is a very abundant polymer.
3D printed objects made of cellulose would biodegradable and could even capture
carbon dioxide that would otherwise pollute the atmosphere.
Paul Gatenholm, a
professor of bio-polymer technology at Chalmers and one of the study authors,
envisions a huge range of applications for products printed with cellulose.
"Potential applications range from sensors integrated with packaging, to
textiles that convert body heat to electricity, and wound dressings that can
communicate with healthcare workers," he says. In the future his team
plans to experiment with other organic compounds derived from wood.



















